Table of Contents
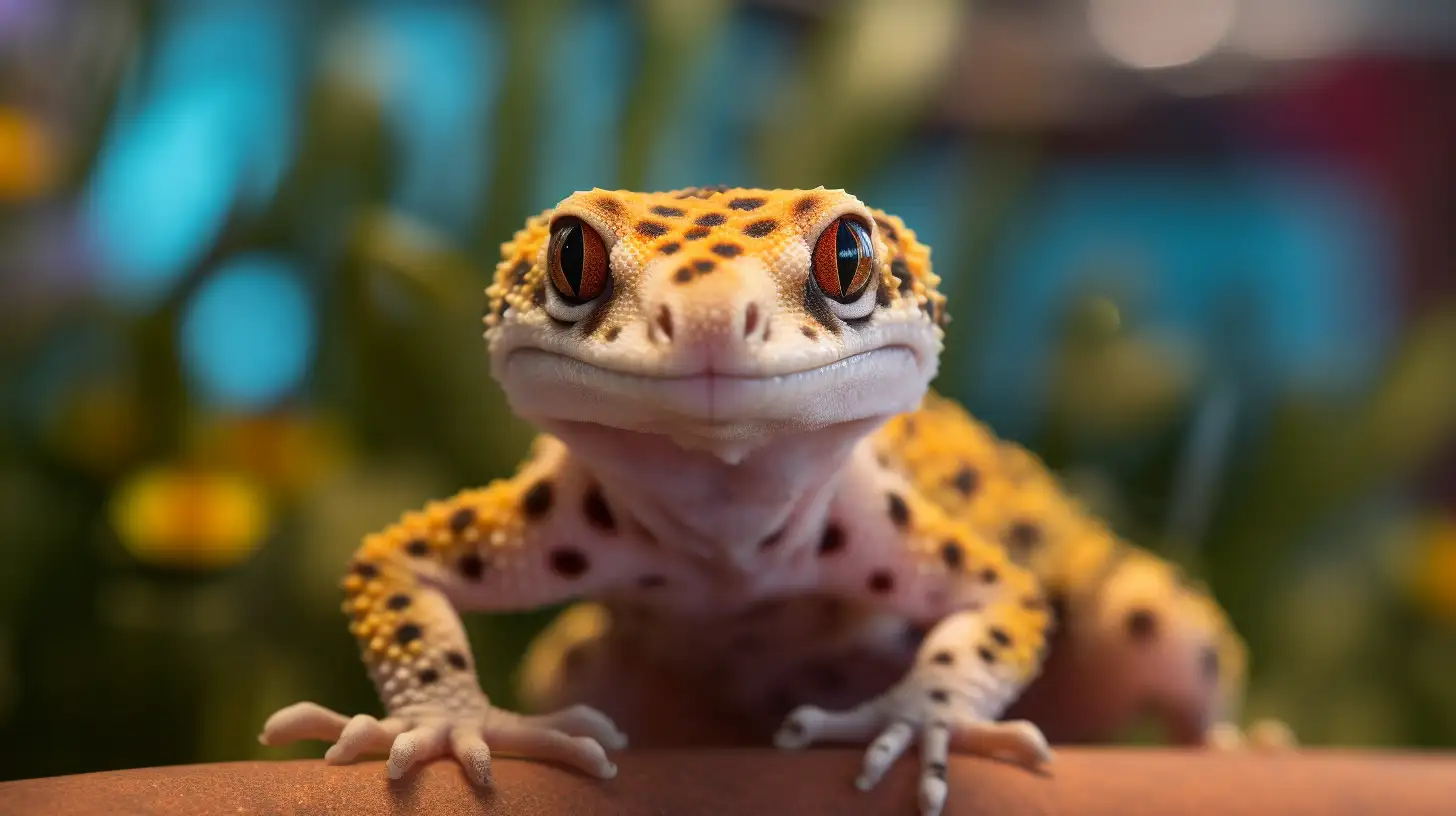
It’s not unusual for a leopard gecko owner to occasionally ask, “why is my leopard gecko not eating?” Leopard geckos are generally voracious eaters, and a sudden loss of appetite can be a cause for concern. This comprehensive guide aims to provide insights into the many factors that could lead to this situation, helping owners ensure their pet’s health and wellbeing.
Understanding Leopard Gecko’s Diet
A key aspect of answering the question about why a leopard gecko might not be eating lies in understanding what makes up a healthy diet for these creatures. Leopard geckos are insectivores, meaning they thrive on a diet of insects. Favorites typically include mealworms, waxworms, crickets, and dubia roaches. Some may even enjoy the occasional silkworm or hornworm. Variety is important, as each type of insect offers different nutritional values.
are insectivores, meaning they thrive on a diet of insects. Favorites typically include mealworms, waxworms, crickets, and dubia roaches. Some may even enjoy the occasional silkworm or hornworm. Variety is important, as each type of insect offers different nutritional values.
Common Reasons for Appetite Loss in Leopard Geckos
Let’s delve into some of the more common reasons why your leopard gecko may not be eating.
Stress
Stress can play a significant role in the loss of appetite in leopard geckos. Changes in their environment, such as a move to a new habitat, the presence of new pets or people, or excessive handling, can all induce stress. Similarly, an inappropriate habitat – too small, too crowded, or lacking in proper hideouts – can also cause anxiety. Stress can, therefore, be a significant factor in understanding a leopard gecko is not eating.
Illness
These lizards , like all creatures, may lose their appetite when they are feeling unwell. Several health issues could lead to this condition. These include parasites, infections, metabolic bone disease, or impaction, a potentially severe condition where the digestive tract is blocked (often due to ingesting substrate).
, like all creatures, may lose their appetite when they are feeling unwell. Several health issues could lead to this condition. These include parasites, infections, metabolic bone disease, or impaction, a potentially severe condition where the digestive tract is blocked (often due to ingesting substrate).
Signs of Dehydration
Understanding the signs of dehydration is essential for any leopard gecko owner. Dehydration can indeed affect a leopard gecko’s appetite, causing them to eat less than usual or stop eating entirely.
Just like in humans, water is a vital component of a leopard gecko’s body, facilitating numerous biological processes, including digestion. When they don’t get enough water – whether due to a lack of drinking, excessive heat, low humidity, or a health condition – dehydration can set in.
Typical signs of dehydration in leopard geckos include sunken eyes, lethargy, loss of skin elasticity, and wrinkled skin. In more severe cases, they might also display a lack of coordination. When pinched gently, the skin of a well-hydrated gecko will quickly return to its normal position, while the skin of a dehydrated gecko may remain tented or slowly return to its regular state.
In the wild, leopard geckos derive much of their moisture from their diet of live insects. However, in captivity, it’s essential to provide a dish of clean, fresh water that’s shallow enough to prevent drowning. The water dish should be placed in the cooler part of the enclosure to discourage bacterial growth.
If you notice signs of dehydration in your leopard gecko, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly to prevent a potential decline in health, including appetite loss. This can include increasing the water supply, misting the habitat to improve humidity, and seeking advice from a vet if symptoms persist. Remember, keeping your pet hydrated is a vital part of ensuring their overall health and well-being.

Seasonal Changes/Breeding Season
Leopard geckos may also experience changes in their eating patterns due to seasonal variations or the breeding season. During colder months, leopard geckos may enter a state of brumation, similar to hibernation, where their metabolic activities slow down, including their appetite. Similarly, during the breeding season, female leopard geckos may eat less due to the stress and energy demands of egg production.
Shedding and Appetite Loss
In the world of leopard geckos, it’s not uncommon to notice a sudden dip in appetite during their shedding periods. Shedding, or ecdysis, is a natural process for these reptiles , as it allows them to remove old skin and grow. However, it can also be a time of discomfort and stress, which can have a direct impact on their eating patterns.
, as it allows them to remove old skin and grow. However, it can also be a time of discomfort and stress, which can have a direct impact on their eating patterns.
For leopard geckos, shedding usually occurs once every four to six weeks, and during this time, they may exhibit a variety of behaviors related to the shedding process. You may notice your gecko rubbing against objects in its enclosure to help loosen the old skin. They might also become more reclusive, spending more time in the hideouts in their habitat.
This change in behavior is often accompanied by a loss of appetite. The process of shedding requires energy and can cause discomfort, leading your gecko to prioritize shedding over eating. It’s not unusual for a leopard gecko to skip meals or eat less during this period. However, normal appetite usually resumes once the shedding is complete.
It’s important to note that while shedding is a normal process, it should be closely monitored. Problems with shedding, such as dysecdysis (abnormal or difficult shedding), can cause additional stress and health problems. If you notice your leopard gecko struggling with shedding or not eating for an extended period, it’s crucial to seek professional advice to ensure their health and well-being.
Age-Related Appetite Changes
As living creatures, leopard geckos undergo various changes as they age, and one such change is a shift in their eating habits. Much like humans, their metabolism tends to slow down as they get older, which naturally leads to a decrease in food consumption.
In their younger years, leopard geckos are quite voracious and enjoy a steady diet of insects. However, as they transition into their mature years, don’t be alarmed if they start showing less interest in their meals. This doesn’t necessarily indicate a problem – it’s a normal part of aging for them.
It’s essential to adjust their feeding schedules and quantities accordingly as overfeeding an older gecko can lead to obesity, which comes with its own set of health issues. Monitoring their weight and physical condition becomes particularly important in these later stages of their life.
However, a drastic or sudden loss of appetite is still a cause for concern and should not be overlooked. Even though older geckos eat less, they should still show interest in food and maintain a healthy weight. If you notice any severe changes, it’s best to consult a professional to rule out any underlying health issues.
Age-related changes in a leopard gecko’s diet are a natural part of their life cycle. Understanding these changes and adjusting their care accordingly will help ensure your gecko remains happy and healthy throughout their golden years.
Here’s a table that breaks down some possible reasons for why a leopard gecko might not eat:
| Reason | Description | Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Stress | Changes in the environment, handling, or presence of other pets can stress leopard geckos. | Create a stress-free environment. Minimize handling and introduce changes slowly. |
| Illness | Health issues, such as parasitic infection, metabolic bone disease, or impaction can cause loss of appetite. | Consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment. |
| Incorrect Habitat Conditions | Incorrect temperature, lighting, or a dirty environment can cause stress and lead to loss of appetite. | Ensure optimal habitat conditions including correct temperature gradient, a proper light-dark cycle, and regular cleaning. |
| Seasonal Changes/Breeding Season | Leopard geckos may eat less during colder months or the breeding season. | Understanding these natural cycles can help. Consult a vet if the gecko refuses to eat for extended periods. |
| Inadequate Diet | Feeding the same type of insect repeatedly or offering improper food can cause a loss of interest in eating. | Offer a variety of insects to provide a balanced diet. |
| Age | As leopard geckos age, their metabolism slows down, which can lead to decreased appetite. | This is a natural process, but drastic changes should be discussed with a vet. |
| Dehydration | Lack of access to fresh water or low humidity levels can lead to dehydration, affecting appetite. | Provide a dish of fresh water and maintain appropriate humidity levels. |
| Shedding | Leopard geckos often eat less or refuse food entirely when they are about to shed. | This is a normal process. Continue to offer food and ensure the habitat has appropriate humidity for a comfortable shed. |
Impact of Incorrect Habitat Conditions
In the quest to understand why your leopard gecko is not eating, it’s crucial not to overlook the impact of their habitat conditions.
Temperature
Leopard geckos are ectothermic animals, meaning they rely on external sources for body heat. This factor plays a vital role in their digestion process. If the habitat is too cold, leopard geckos can’t digest their food properly, leading to a loss of appetite. Conversely, if it’s too hot, it can cause undue stress leading to the same result.
Lighting
While leopard geckos, being nocturnal, do not require special UV lighting, it’s essential to maintain a consistent day-night cycle in their habitat. Constant light or dark can disrupt their natural rhythms and potentially affect their eating habits.
Space and Cleanliness
A habitat that is too small, overcrowded, or not clean can contribute to stress and result in your leopard gecko not eating. Regular cleaning of the habitat, providing ample space, and ensuring a clutter-free environment can encourage healthy eating behaviors.
No products found.
Importance of Regular Vet Checkups
Even with diligent care, it’s possible to miss subtle signs of illness or distress in your leopard gecko that may lead to appetite loss. Regular vet check-ups can play a significant role in maintaining the health of your pet. A professional can perform routine checks, diagnose potential health issues, and provide advice and treatment options, all of which can address the concerns of not eating.
How to Encourage Eating in Leopard Geckos
If you’re facing the issue of your leopard gecko not eating, here are some strategies that could help stimulate their appetite.
Suggested Changes in Feeding Habits
Sometimes, merely varying the diet can be enough to reignite a leopard gecko’s interest in food. Try introducing different types of insects into their diet or changing the feeding frequency slightly. It’s important to remember not to leave uneaten food in the gecko’s enclosure, as this can attract parasites and lead to stress or illness.
Appropriate Feeding Schedule for Leopard Geckos
It is crucial to examine if the feeding schedule aligns with their natural habits and needs. Leopard geckos are primarily nocturnal animals, meaning they’re most active during the night. Consequently, feeding them late in the evening or at night often yields the best results.
However, the frequency and quantity of feeding can greatly depend on the gecko’s age. For example, younger geckos, especially hatchlings and juveniles, have faster metabolisms and are growing, requiring more frequent feedings. Ideally, they should be fed once a day, with as many insects as they can eat in 15 minutes.
On the other hand, adult leopard geckos may be fed every other day or even every third day, depending on their individual metabolism and appetite. Generally, offering them 2-5 appropriately sized insects during each feeding session is suggested.
In terms of portion size, a good rule of thumb is that the width of the food item should not exceed the space between the gecko’s eyes. Offering insects that are too large can risk causing impaction or digestive distress.
Remember, dusting the insects with a high-quality calcium and vitamin D3 supplement before feeding is an important part of the leopard gecko’s diet. This helps prevent Metabolic Bone Disease, a common illness in captive reptiles.
Creating a Stress-Free Environment
Minimizing stress is crucial in encouraging a leopard gecko to eat. Ensure that their habitat is quiet, clean, and appropriately sized, with plenty of hiding places. If your gecko appears particularly anxious or stressed, try limiting handling until they seem more relaxed.
Maintaining Optimal Habitat Conditions
Keeping the habitat conditions within the ideal range for leopard geckos can also be beneficial. The temperature should be properly controlled, with a warm end for basking (around 88-92 degrees Fahrenheit) and a cooler end for resting (around 75-80 degrees Fahrenheit). Additionally, maintaining a regular day-night light cycle can also encourage natural behavior, including eating.

When to Seek Professional Help
It’s essential for every leopard gecko owner to understand when professional help may be required. Recognizing the signs that something is not quite right with your pet is the first step in ensuring their well-being.
Prolonged Loss of Appetite
While occasional appetite loss is not uncommon in leopard geckos, if your gecko refuses to eat for an extended period (more than a week), it might be time to consult a vet. Prolonged appetite loss can indicate serious underlying issues such as illness, severe stress, or improper habitat conditions.
Observable Changes in Behavior
Any observable change in your gecko’s behavior is worth noting. Changes could include increased lethargy, aggression, hiding more than usual, or unusual reactions to handling. These could be signs of discomfort, stress, or disease.
Changes in Physical Appearance
Leopard geckos can display a range of physical symptoms when unwell. These may include weight loss, unusually soft or discolored feces, changes in skin color, irregular shedding, or visible parasites. Swollen or closed eyes, a swollen belly, or a limp tail can also be signs of distress.
Ingesting Non-food Items
If you notice your leopard gecko ingesting non-food items, like substrate, it’s important to seek immediate professional help. This behavior can lead to impaction, a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
If you observe any of these signs or any other unusual behavior, it’s crucial to consult a reptile-savvy vet promptly. It’s always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to the health of your pet. Regular veterinary check-ups are invaluable, but being proactive and seeking help when necessary can make all the difference in ensuring the health and happiness of your leopard gecko.
Potential Treatments for Appetite Loss in Leopard Geckos
When a leopard gecko is not eating, it’s vital to not only identify the potential causes but also to explore appropriate treatments. Here are some potential treatments based on the primary causes of appetite loss discussed earlier in the article.
Stress-Related Appetite Loss
For stress-induced appetite loss, one of the most effective treatments is improving the habitat conditions and reducing environmental stressors. This might involve optimizing the temperature gradient, maintaining a proper light-dark cycle, increasing the size of the enclosure, or introducing more hideouts. Limiting handling until the gecko’s appetite returns can also be beneficial.
Illness-Related Appetite Loss
If the appetite loss is due to an illness such as parasitic infection, metabolic bone disease, or impaction, it’s highly recommended to consult with a veterinarian. They may prescribe medications, suggest dietary changes, or in severe cases, recommend surgical intervention. Always remember that home remedies should not replace professional veterinary advice and treatment.
Dehydration and Appetite Loss
If dehydration is suspected, providing a shallow dish of fresh, clean water in the enclosure can be helpful. Increasing the humidity level by misting the enclosure can also assist in rehydration. However, severe cases of dehydration should always be addressed by a veterinarian.
Age or Shedding Related Appetite Loss
In the case of appetite loss due to natural causes like aging or shedding, patience and understanding are often the best treatments. Continue to offer food and ensure the gecko’s environment is comfortable and stress-free. However, if the gecko continues to refuse food for an extended period, it’s best to seek veterinary advice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the question “why is my leopard gecko not eating” involves looking at several factors, including diet, stress levels, potential illness, and habitat conditions. By paying close attention to these elements, you can ensure that your pet remains healthy and has a robust appetite. Always remember that when in doubt, it’s best to seek professional veterinary advice. Leopard geckos are resilient creatures, and with the right care and attention, they can overcome most hurdles, including a loss of appetite. Embrace the journey of understanding your leopard gecko’s needs and providing them with a healthy, happy life.
Key Takeaways
- Leopard geckos are insectivores and require a variety of insects in their diet.
- A lack of appetite in leopard geckos can be caused by stress, dehydration, shedding, aging, or inappropriate habitat conditions.
- It is important to provide a clean, fresh-water dish and maintain appropriate temperatures and humidity levels in their habitat.
- Regular veterinary check-ups can help prevent and address any health issues.
- Patience and a stress-free environment can help address appetite loss due to natural causes such as aging or shedding.
FAQs
Q: What should I do if my leopard gecko refuses to eat?
A: First, don’t panic. Observe your gecko for a day or two to confirm if the loss of appetite persists. If it does, evaluate the conditions of its habitat, check for signs of illness or stress, and consider any recent changes in its environment. If the situation doesn’t improve or if your gecko exhibits other concerning symptoms, consult with a vet.
Q: Can stress cause my leopard gecko to stop eating?
A: Yes, stress is a common reason for appetite loss in leopard geckos. Changes in their environment, such as a new habitat, the presence of new pets or people, or excessive handling, can all induce stress and potentially cause your gecko to stop eating.
Q: What illnesses might cause my leopard gecko to stop eating?
A: Several health issues could lead to appetite loss, including parasites, infections, metabolic bone disease, impaction, or dehydration. If you suspect illness as the reason for your gecko not eating, it’s recommended to seek professional veterinary advice.
Q: Can seasonal changes affect my leopard gecko’s appetite?
A: Yes, during colder months, leopard geckos may enter a state of brumation, a period of reduced activity similar to hibernation. During this time, their metabolic activities slow down, including their appetite. Additionally, during the breeding season, female geckos may eat less due to the stress and energy demands of egg production.
Q: Can incorrect habitat conditions affect my leopard gecko’s eating habits?
A: Absolutely. Temperature, lighting, and the cleanliness of the habitat can all significantly impact a leopard gecko’s eating habits. If their habitat is too cold, they might not be able to digest food properly, leading to a loss of appetite. Conversely, if it’s too hot, it can cause undue stress.
Q: How can I encourage my leopard gecko to start eating again?
A: You can stimulate your gecko’s appetite by varying its diet, creating a stress-free environment, and maintaining optimal habitat conditions. However, if your gecko continues to refuse food, consult with a vet.
Q: Should I force feed my leopard gecko if it refuses to eat?
A: It’s generally not recommended to force-feed your gecko as this could cause additional stress and potential injury. Instead, try addressing the underlying causes of appetite loss and consult with a vet if you’re concerned.
Q: How often should I feed my leopard gecko?
A: Young geckos usually eat daily, while adults can be fed every other day. However, this can vary based on individual needs and the gecko’s overall health.
Q: Can aging affect my leopard gecko’s appetite?
A: Yes, as leopard geckos age, their metabolism can slow down, leading to decreased food consumption. This is a natural process, but if the reduction in appetite seems sudden or drastic, it’s worth consulting with a vet.
Q: When should I seek professional help for my leopard gecko’s loss of appetite?
A: If your leopard gecko’s loss of appetite persists for more than a week, or if it’s accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as lethargy, weight loss, changes in stool, or visible signs of illness, it’s important to seek professional veterinary advice.
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Please be advised that all images, designs, and creative content on this page are the exclusive property of JustExoticPets.com and are protected under international copyright laws. The images may not be reproduced, copied, transmitted or manipulated without the written permission of JustExoticPets.com.
and are protected under international copyright laws. The images may not be reproduced, copied, transmitted or manipulated without the written permission of JustExoticPets.com.
Unauthorized use, distribution, display, or creation of derivative works of any images contained on this site, is strictly prohibited and can lead to legal penalties. We actively monitor for, and enforce, our copyright interests.
If you wish to use any of our images, kindly contact us to seek permission. Respect of copyright is not merely a legal requirement but also an acknowledgement and support of the hard work and creativity that goes into producing them.
Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.
© 2023, JustExoticPets.com. All Rights Reserved.

